


Table of Contents
With Space Cloud, you can trigger webhooks on any custom events in your application. Space Cloud uses an in-built eventing queue to invoke your webhooks reliably.
Open a project in Mission Control, head to the Event Triggers section and click on the Add button to open the form below:

Trigger Name
Give a unique name for an event trigger. (e.g., welcome-email )
Source
Select Custom as the event source.
Type
The type of event for which you want to create a trigger. (eg: sent-email). Whenever, an event of a particular type is queued, all event triggers registered with that type are triggered.
Webhook URL
The HTTP(s) URL that should get triggered with the event payload on the configured operation. Must be a POST handler.
Retries
The number of times to retry a failed invocation. Default value is 3.
Timeout
Timeout in milliseconds. Default value is 5000.
You can trigger your custom event either via Mission Control or programmatically via the HTTP API of Space Cloud. You can also schedule an event for the future.
To deliver/queue an event to Space Cloud, make an HTTP POST request to Space Cloud:
Endpoint:
http://<space-cloud-url>/v1/api/<project-id>/event-triggers/queueJSON payload:
{
"type": "<event-type>",
"delay": "Number",
"timestamp": "Number",
"data": "Object"
}| Key | Type | Required | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| type | String | yes | Type of event. | |
| timestamp | Number | no | Used to schedule event trigger at the given timestamp (in milliseconds) schedule time for event trigger. | |
| delay | Number | no | 0 | Number of seconds to delay the trigger from timestamp. |
| data | Object | no | null | Event data. |
For example,
{
"type": "sent-email",
"data": {
"to": "user1@email.com",
"from": "user2@email.com",
"subject": "Some Subject"
}
}You can schedule events to be triggered later by using timestamp and/or delay fields:
Example: Delay event trigger by 1 minute:
{
"type": "my-custom-event",
"delay": 3600,
"data": {
"foo": "bar"
}
}Example: Schedule event trigger for a particular time:
{
"type": "my-custom-event",
"timestamp": 1587902400,
"data": {
"foo": "bar"
}
}Example: Delay event trigger by 1 minute from a particular time:
{
"type": "my-custom-event",
"delay": 3600,
"timestamp": 1587902400,
"data": {
"foo": "bar"
}
}Custom event triggers can be invoked via the Mission Control as well.
Head to the Event Triggers section and click the Trigger button for any event trigger in the Actions column to open the following form:
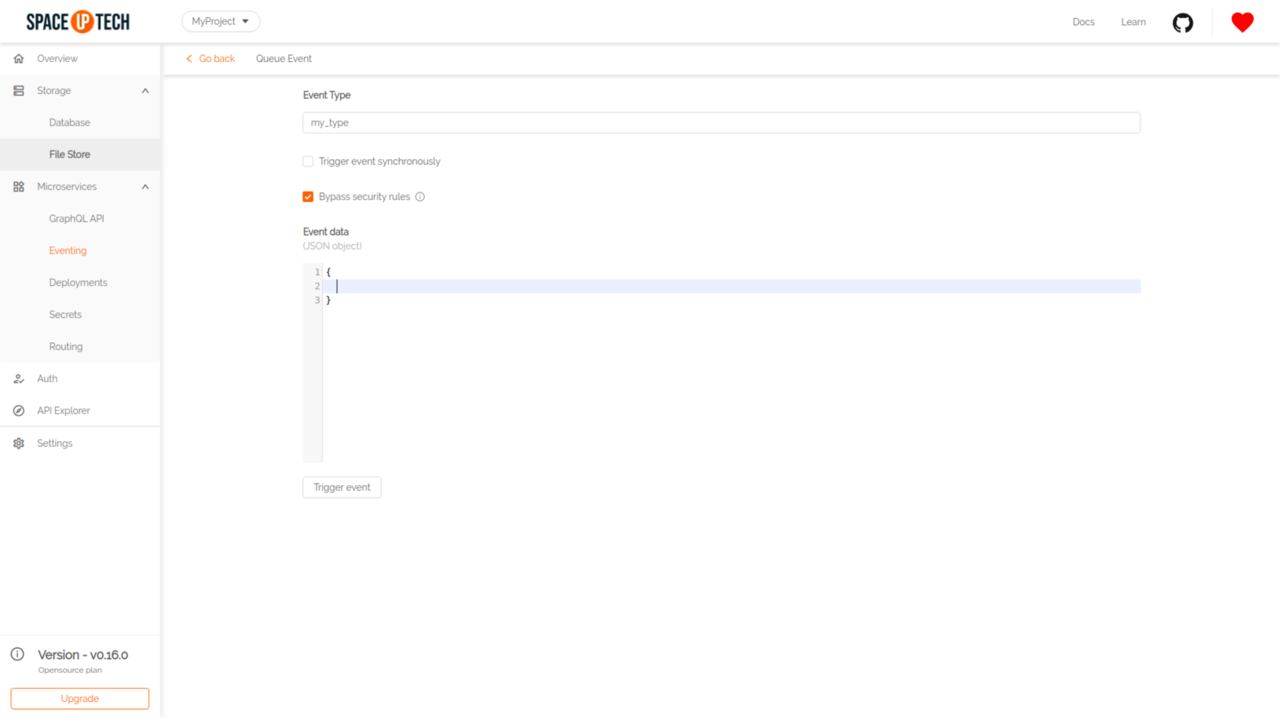
Put the event data and hit Trigger.
The webhook is delivered over HTTP POST request to the specified webhook URL with the following headers:
Content-Type: application/jsonThe POST body of the webhook is a JSON object which follows the Cloud Events specs:
{
"specversion": "1.0-rc1",
"id": "<unique-uuid>",
"type": "<event-type>",
"source": "<space-cloud-node-id>",
"time": "<date-string>",
"data": "Object"
}| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| specversion | String | Version of the Cloud Events specifications. |
| id | String | A unique identifier of an event. |
| type | String | Event type. |
| source | String | Unique identifier of a Space Cloud instance. |
| time | String | Time at which the event occurred(ISO 8601 format). |
| data | Object | Event data sent by the client. |
For example,
{
"specversion": "1.0-rc1",
"id": "43e32d79-f2bf-41c0-be5f-a75c8c1bcfbf",
"type": "my-custom-event",
"source": "1fb07d5d-b670-468e-ba94-ad5f06a5c053",
"time": "2019-10-19T12:40:50.053Z",
"data": {
"foo": "bar"
}
}A 2xx response status code from the webhook target is deemed to be a successful invocation of the webhook. Any other response status results in an unsuccessful invocation that causes retries as per the retry configuration.